|
| Anthidiellum (Ranthidiellum) phuchongensis Nalinrachatakan & Warrit, in Nalinrachatakan, Traiyasut, Khongnak, ... et Warrit, 2021. |
Abstract
Resin bees of the subgenus Ranthidiellum, are rare and endemic to Southeast Asia. These bees are known to construct resinous entrance tubes to their nests. Here, the new species Anthidiellum (R.) phuchongensis sp. nov. is described along with a description of its nest collected from Phu Chong Na Yoy National Park, Ubon Ratchathani Province, Thailand. In addition, the bee cleptoparasite, Stelis (Malanthidium) flavofuscinular sp. nov., and the male of A. (R.) ignotum Engel, 2009, are described for the first time. A key to Ranthidiellum species is also provided.
Keywords: Anthidiellum, Malanthidium, pollinator, systematics, taxonomy, wool carder bee
Anthidiellum (Ranthidiellum) phuchongensis Nalinrachatakan & Warrit, sp. nov.
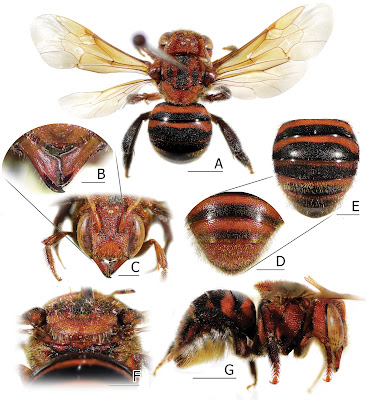
Diagnosis: This new species resembles Anthidiellum ignotum Engel, 2009 in overall appearance, but differs by its dark orangish to reddish integument; facial marks restricted on the frons; black apical bands on all terga except T6, making T6 clearly orangish (Fig. 3D), whereas all other females of Ranthidiellum species come with black T6; black hairs on T2, T3, and lateral of T1 and T4; black hind coxa on the upper part with a small black patch around its lower part. Midleg and hindleg covered with black hairs on tibia and basal part of tarsi, making these legs superficially brownish; male S4 gradulus complete.
Etymology: The name is given to the Phu Chong Na Yoy National Park, Ubon Ratchathani Province, where both the holotype and paratype were collected. ผึ้งหยาดอำพันภูจอง
Floral association: Dipterocarpaceae. It is evident that A. phuchongensis utilized resins of Dipterocarpus obtusifolius Teijsm. ex Miq., a dominant plant in the area.
Bee kleptoparasites: Stelis flavofuscinular sp. nov. (see below).
Genus Stelis Panzer, 1806
Subgenus Malanthidium Pasteels, 1969
Malanthidium Pasteels, 1969: 26.
Type species: Anthidium malaccense Friese, 1914, by original designation.
Stelis (Malanthidium) flavofuscinular Nalinrachatakan & Warrit, sp. nov.
Diagnosis: With only males known, Stelis flavofuscinular is distinct from its only known congener, S. malaccensis from Malaysia, as follows: head overall black, with yellow paraocular mark reaching close to the top of eyes, and narrow mark restricted close to apical area of clypeus; antennal scape black; Mesosoma overall black except yellow on postero-lateral hook of axilla; T1–T5 with large yellow strike band, with little median disruption that is pronounced more on rear metasomal segments; T6 with lateral yellow dots; S2–S4 with distinct median patch of long white hairs, while lacking black midapical comb. S4 and genitalia as in Fig. 7G.
Etymology: The word flavo means “yellow”, while fuscinular means “hook”. Thus, the specific epithet, flavofuscinular, principally refers to the yellow postero-lateral axilla hook of male bees that contrasts with its overall black mesosoma. ผึ้งบุษราคัม
Bee host: Anthidiellum phuchongensis sp. nov. (see above). It is possible that S. flavofuscinular sp. nov. may also be a cleptoparasite of other Megachile species that are also frequently encountered in the PCNYNP area. Kasparek (2015) suggested that the hosts of Stelis species are mainly members of Megachilinae, and some Stelis species have a wide range of hosts.
Pakorn Nalinrachatakan, Prapun Traiyasut, Anupong Khongnak, Manop Muangkam, John S. Ascher and Natapot Warrit. 2021. The Resin Bee Subgenus Ranthidiellum in Thailand (Megachilidae, Anthidiini): Nesting Biology, Cleptoparasitism by Stelis, and New Species. ZooKeys. 1031: 161-182. DOI: 10.3897/zookeys.1031.57836
การค้นพบผึ้งชนิดใหม่ของโลกจากอุทยานแห่งชาติภูจองนายอย จังหวัดอุบลราชธานี
ผึ้งหยาดอำพันภูจอง (Phujong Resin Bee) หรือ Anthidiellum (Ranthidiellum) phujongensis n. sp. เป็นผึ้งเฉพาะถิ่น อุทยานแห่งชาติภูจองนายอย และพบได้เพียงที่เดียวเท่านั้นบนโลก โดยอาศัยอยู่ในรังบนผาดิน ใช้ยางไม้สร้างรังและปากทางเข้า ภายในรังจะมีผึ้งตัวเมียเพียงตัวเดียวที่ทำหน้าที่ทุกอย่างตั้งแต่สร้างรัง วางไข่ และออกหาอาหารให้กับตัวอ่อน
พร้อมกันนี้ทีมผู้วิจัยยังได้ค้นพบผึ้งปรสิตชนิดใหม่ของโลก ภายในรังของผึ้งหยาดอำพันภูจองอีกด้วย โดยได้ทำการตั้งชื่อว่า ผึ้งบุษราคัม (Topaz Cuckoo Bee) หรือ Stelis (Malanthidium) flavofuscinular n. sp. โดยผึ้งชนิดนี้จะแอบวางไข่ในรังของผึ้งหยาดอำพันและแย่งอาหารของลูกผึ้งหยาดอำพันกิน