 |
| Aliaporcellana spongicola
Hiller & Werding, 2018
|
Abstract
Aliaporcellana spongicola sp. n. from the Philippines and Indonesia is described. The new species has been frequently photographed by divers because of its striking coloration, but has not been described yet. Aliaporcellana spongicola sp. n. is in fact a widespread commensal of barrel sponges of the genus Xestospongia and other sponges. Morphological characters and ecological information of all described species of Aliaporcellana, and of other porcellanids associated with sponges and soft corals, suggest that all members of the genus are commensals, and that similar morphological adaptations to dwelling on these hosts have evolved independently in different evolutionary lines within Porcellanidae.
Keywords: Crustacea, Porcellanidae, Aliaporcellana, new species, Indo-West Pacific, commensalism, adaptation, sponge- and octocoral-dwelling
Systematic account
Family Porcellanidae
Aliaporcellana spongicola sp. n.
Description:
Carapace rounded (Figures 1, 2), considerably variable in form and in length-width ratio; larger females with carapace broader than long (ratio < 1), smaller individuals with carapace relatively longer than broad (ratio > 1); dorsal surface convex, glossy, with faint, transverse striae on branchial and intestinal regions; cervical grooves gently depressed. Front (Figures 1, 2) broad, slightly produced beyond eyes, weakly trilobate, somewhat deflexed; frontal lobe visible in dorsal view, grooved, overreaching lateral ones. Distal margin of entire front lined with row of rounded, upwardly directed small spines (Figure 3a), the largest on supraocular edges. Outer orbital angles (Figure 2) forming acute, bifid tooth followed by hepatic spine of similar size. Epibranchial margin rounded, produced outwards, marked with epibranchial spine; cervical groove faintly marked. Mesial branchial margins crested, with row of 5 or 6 strong, anteriorly, upwardly directed spines of increasing size posteriorly. Sidewalls entire.
Eyes moderately large (Figures 1, 2, 3a), retracted, ocular peduncles short. First movable segment of antennal peduncle (Figures 2, 3b) with strong, anteriorly curved distal spine, second with smaller, anterodistal, acute protuberance, third one globular. Basal segment of antennular peduncle (Figure 3c) with anterior surface transversely rugose, surrounded with open ring of strong, conical spines. Third maxilliped (Figure 3d) slightly rugose, ischium sub-quadrate with inner lobe, inner margin of merus semi-circular; exopodite long, pyriform, reaching 2/3 of length of merus.
 |
| Figure 2. Aliaporcellana spongicola sp. n. Female (ovigerous) holotype, UF 43328, Philippines, Oriental Mindoro Province, Mindoro, Puerto Galera, off Pt W of Bayanar Beach. Scale bar: 2 mm. |
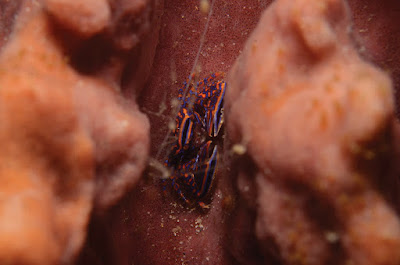 |
| Figure 5. Aliaporcellana spongicola sp. n. Live specimen sitting on barrel sponge (photograph UF dPHIL 09927). Same collection data as holotype. |
Ecology: Aliaporcellana currently consists of six species. Of all species, A. spongicola sp. n. is by far the most strikingly colorful, and has, therefore, become popular among underwater photographers and marine aquarists. Aliaporcellana spongicola sp. n. dwells on large barrel sponges of the genus Xestospongia Laubenfels [family Petrosiidae; e.g., X. testudinaria (Lamarck 1815)] and on other types of sponges, like the “large, grey foliose sponge”, on which the crabs from Sulawesi included in this study, were found. The porcellanid lies in the sponge’s folds, where it is most protected from predators (Figure 5).
Distribution: The type specimens come from the central Philippines and northern Sulawesi, Indonesia.
Etymology: The name spongicola (from the Latin word spongia, meaning sponge, and the Latin suffix -cola, meaning dwelling) refers to the sponge-dwelling habit of the new species.
Remarks: Aliaporcellana spongicola sp. n. is considerably variable in the shape of carapace and the degree of spination on body and extremities. As in other porcellanid species, the spines are more defined in smaller specimens. The new species is distinguished from A. pygmaea and A. kikuchii by the lack of acute spines on the dactylus of the smaller cheliped (Osawa 2007; Dong et al. 2011), and by its smoother surface of carapace and chelipeds (Lewinsohn 1969; Nakasone and Miyake 1969; Werding and Hiller 2007; Osawa and Chan 2010). Aliaporcellana spongicola sp. n. can be distinguished from A. suluensis, A. telestophila and A. taiwanensis by its regularly denticulated front (Figures 2, 3a), which is smooth in the other species, and by the basis of the antennular peduncle, which is crowned with a ring of spines (Figure 3c) and is at most granulate or faintly serrate in the compared species (see Lewinsohn 1969; Werding and Hiller 2007; Dong et al. 2011 for A. suluensis; Ng and Goh 1969 for A. telestophila; Dong et al. 2011 for A. taiwanensis).
Alexandra Hiller and Bernd Werding. 2018. On A New Commensal Species of Aliaporcellana from the western Pacific (Crustacea, Decapoda, Porcellanidae). ZooKeys. 780: 1-9. DOI: 10.3897/zookeys.780.26388

