Highlights
• Increased density of subspecific taxon sampling and complementary biometric analysis clarifies sister species relationships in tits.
• Our genetic assignment of type specimens proves a sister group relationship between P. weigoldicus and P. montanus.
• We refute the hypothesis of a close relationship between P. montanus and P. hypermelaenus who is sister to P. palustris.
• Haplotype distribution suggests mitochondrial introgression among P. hypermelaenus and Eastern Palearctic P. palustris.
• P. songarus is paraphyletic and treatment as a separate species does not conform to various species concepts.
• Patterns of biometric and genetic differentiation are congruent in P. palustris but not in P. montanus.
Abstract
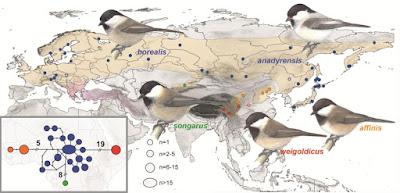
A recent full species-level phylogeny of tits, titmice and chickadees (Paridae) has placed the Chinese endemic black-bibbed tit (Poecile hypermelaenus) as the sister to the Palearctic willow tit (P. montanus). Because this sister-group relationship is in striking disagreement with the traditional affiliation of P. hypermelaenus close to the marsh tit (P. palustris) we tested this phylogenetic hypothesis in a multi-locus analysis with an extended taxon sampling including sixteen subspecies of willow tits and marsh tits. As a taxonomic reference we included type specimens in our analysis. The molecular genetic study was complemented with an analysis of biometric data obtained from museum specimens. Our phylogenetic reconstructions, including a comparison of all GenBank data available for our target species, clearly show that the genetic lineage previously identified as P. hypermelaenus actually refers to P. weigoldicus because sequences were identical to that of a syntype of this taxon. The close relationship of P. weigoldicus and P. montanus – despite large genetic distances between the two taxa – is in accordance with current taxonomy and systematics. In disagreement with the previous phylogenetic hypothesis but in accordance with most taxonomic authorities, all our P. hypermelaenus specimens fell in the sister clade of all western and eastern Palearctic P. palustris. Though shared haplotypes among the Chinese populations of the two latter species might indicate mitochondrial introgression in this part of the breeding range, further research is needed here due to the limitations of our own sampling.
Keywords: Poecile hypermelaenus; Poecile weigoldicus; multi-locus phylogeny; phylogeography; DNA barcoding
Christian Tritsch, Jochen Martens, Yue-Hua Sun, Wieland Heim, Patrick Strutzenberger and Martin Päckert. 2017. Improved Sampling at the Subspecies Level Solves A Taxonomic Dilemma - A Case Study of Two Enigmatic Chinese Tit Species (Aves, Passeriformes, Paridae, Poecile) Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. In Press. DOI: 10.1016/j.ympev.2016.12.014