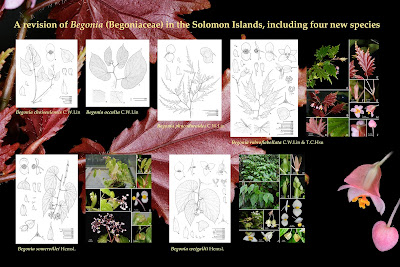
|
| Begonia rubroflabellata C.W. Lin & T.C. Hsu., in Lin, Hsu, Yang, Fanerii, Pittisopa et Li, 2021. |
Abstract
The Solomon Islands in Melanesian region of South Pacific lie in an equatorial climate and harbour diverse habitats covered by forests. Based on field surveys and specimens examination, six Begonia species were confirmed from the Solomon Islands, and a key of the species is provided for identification. Besides the two widespread species, B. somervillei Hemsl. and B. weigallii Hemsl., four new species, B. choiseulensis, B. occulta, B. phycoduroides and B. rubroflabellata, are described and illustrated. All species belong to sect. Petermannia, and five are endemic to the Solomon Islands. Their conservation status following IUCN criteria are also assessed.
Keyword: Begoniaceae, biodiversity, endemism, Melanesia, new record, Petermannia, taxonomy
 |
| Distribution map of Begonia species in the Solomon Islands. Begonia choiseulensis (◼), B. occulta (▲), B. phycoduroides (⬢), B. rubroflabellata (▼), B. somervillei (★) and B. weigallii (●). |
Begonia choiseulensis C.W. Lin, sp. nov.
Diagnosis: Most resembling Begonia weigallii Hemsl. in its erect stems, glabrous ovate leaves and 2-tepaled staminate flowers, but different in its smaller stature, ca. 30 cm tall (vs. often to 100 cm or taller), smaller leaves that are 5–9 cm (vs. usually more than 10 cm, up to 36 cm) long, and persistent (vs. deciduous) stipules and bracts.
Distribution and ecology: Begonia choiseulensis is only known from the Sirovaga area of Choiseul Island. Plants growing on semi-shaded moist limestone cliffs or outcrops at lowland evergreen forest, up to 800 m elevation.
Etymology: Named after its type locality, Choiseul Island.
Begonia occulta C.W. Lin, sp. nov.
Diagnosis: Similar to Begonia torricellensis Warb. in its habit and hairy foliage. However, B. occulta is sharply distinct from B. torricellensis in its stem being hispidvillous up to 2 mm (vs. dense pilose ca. 4 mm) and inflorescence cymose (vs. racemose-cyme). Begonia occulta is also similar to B. vitiensis A.C.Sm., but is distinct in its short-petiolated by 1–4 cm (vs. 10–15 cm), obovate (vs. broadly orbicular) leaves and inflorescence terminal (vs. axillary).
Distribution and ecology: Growing on deeply shaded moist rocks by a stream.
Etymology: The specific epithet occulta means “secret”, because it is known only from the type specimen and was not found in our field works.
 |
| Begonia phycoduroides C.W. Lin. A. Branched habit; B. Stipule; C, C'. Bracts; D. Staminate flower, back view; E. Capsule. |
Begonia phycoduroides C.W. Lin, sp. nov.
Diagnosis: In habit and multi-branched stems and pinnately divided laminae, Begonia phycoduroides is most similar to B. pinnatifida Merr. & L.M. Perry, but the former is different in its 2-pinnatifid (vs. pinnatipartite on the upper half, entire on the lower half) foliage and deciduous (vs. persistent) stipules.
Distribution and ecology: Begonia phycoduroides is endemic to Mt. Sanabe in Choiseul Island. Growing on steep slopes in primary forest at 300 m elevation.
Etymology: The specific epithet is derived from the genus name of Phycodurus eques, the leafy seadragon, and -oides, resembling, referring to the deeply pinnatifid leaves which resemble the leaf-like protrusions on the body of P. eques.
Begonia rubroflabellata C.W. Lin & T.C. Hsu, sp. nov.
Diagnosis: In sharing moderately dissected lamina and 2-tepaled staminate flower, this new species resembles Begonia serratipetala Irmsch. However, B. rubroflabellata is different in its palmatipartite (vs. pinnatifid) leaf blades, entire (vs. toothed) pistillate tepals, and bracteoles present (vs. absent) in the base of ovary.
Distribution and ecology: Begonia rubroflabellata is endemic to the mountainous area around Mt. Popomanaseu in Guadalcanal Island. Plants grow under deeply shaded lower montane forests at elevation 800– 1,000 m.
Etymology: The specific epithet rubroflabellata is derived from the reddish foliage that is fan-shaped.
Begonia somervillei Hemsl., Bull. Misc. Inform. Kew 109: 17 (1896). Type: SOLOMON ISLANDS. Western Province, New Georgia Island, May 1894, B.T. Somerville et al. 222 (holotype K 000761001!).
Distribution and ecology: Begonia somervillei is endemic to the Solomon Islands. It is commonly found growing on steep slopes or along streams from sea level to ca. 850 m elevation.
Begonia weigallii Hemsl., Bull. Misc. Inform. Kew 109: 17 (1896). Type: SOLOMON ISLANDS. Western Province, New Georgia Island, May 1894, S. Weigall et al. 223 (holotype K 000761002!). Begonia salomonensis Merr. & L.M.Perry, J
Distribution and ecology: Begonia weigallii is widespread in the Solomon Islands and Papua New Guinea, including Bougainville and the Bismarck Archipelago (Hughes, 2008). Growing on gentle soil slopes, sandstone or limestone boulders, or on the edge of primeval or secondary forests, from sea level to ca. 1,000 m elevation.
Che-Wei Lin, Tian-Chuan Hsu, Tsung-Yu Aleck Yang, Moffat Fanerii, Fred Pittisopa and Chia-Wei Li. 2021. A Revision of Begonia (Begoniaceae) in the Solomon Islands, Including Four New Species. Taiwania. 66(4); 478 - 495. DOI: 10.6165/tai.2021.66.478