|
| Vitex pomerana Fraga, Antar, J.Freitas & Lírio, in Antar, de Lírio, Freitas & de Fraga, 2022. |
Summary
Vitex comprises c. 250 species in a pantropical distribution, with 34 species recognised for Brazil. During fieldwork in remnants of the Atlantic Forest showing vegetation associated with inselbergs in the state of Espírito Santo, Brazil, a unique, unmatched unifoliolate species of Vitex was found. Based on herbaria consultation and literature review, we propose this as a new species, Vitex pomerana. The new species is unique in the genus due to the presence of unifoliolate leaves, a rare feature in the genus, together with brochidodromous venation of leaflets, dorsifixed anthers, shape and size of leaflets, and petiole and peduncle sizes. We compared the new species with V. gardneriana and V. snethlagiana, the only two other unifoliolate-leaved Vitex species occurring in Brazil. The new species is known from only a few individuals so far and is micro endemic to a biodiversity hotspot that suffers from habitat loss and degradation, and would likely be considered Endangered (EN), based on the criteria of the IUCN red list. This finding increases the number of angiosperm species endemic to the Atlantic Forest and inselbergs in the state of Espírito Santo and highlights the urgency of conserving this highly threatened vegetation.
Key Words: Flora, Labiatae, State of Espírito Santo, Taxonomy, Threatened species
Vitex pomerana Fraga, Antar, J.Freitas & Lírio, sp. nov.
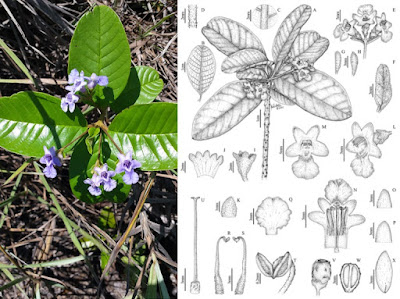
RECOGNITION. The new species resembles Vitex gardneriana and V. snethlagiana by the unifoliolate leaves, from which it differs by presenting a unique combination of elliptic leaflet with apex obtuse to retuse, venation brochidodromous, petiole 4.9 – 8.5 mm long, peduncle 1.45 – 2.6 cm long, and dorsifixed anthers.
ETYMOLOGY. The epithet pomerana (in Portuguese) refers to Pomerania, a historical area in Europe inhabited by a people known as Pomeranians, who spoke the Pomeranian dialect derived from German (not the one derived from a Slavic language, known now as Kashubian, and still spoken in Poland). This region, located in the Southern portion of the Baltic Sea, currently belongs to Germany and Poland. Due to multiple factors, including the WWs and other territorial invasions, the Pomeranians immigrated late in the XIXth century and early in the XXth century mostly to the U.S.A. and Brazil (Clemens 1976; Savedra 2020). Pomeranian descendants are predominant in the mountainous region of Espírito Santo, particularly in the municipalities of Santa Maria de Jetibá and Santa Leopoldina, where there was a significant Pomeranian immigration from 1873 onwards. Nowadays, people from this region still use Pomeranian as their language and maintain part of their cultural traditions (Savedra 2020). Because the new species is restricted to the Espírito Santo mountains, we have decided to honour with the specific epithet the Pomeranian people of Espírito Santo, from which the author EJL is descendent. The use of this epithet is permitted by the Article 23.2 of the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (Turland et al. 2018).
Guilherme Medeiros Antar, Elton John de Lírio, Joelcio Freitas and Claudio Nicoletti de Fraga. 2022.
Vitex pomerana (Lamiaceae; Viticoideae), A New Unifoliolate Species from the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. Kew Bulletin. DOI: 10.1007/s12225-022-10064-x
espiritosantonoticias.com.br/pesquisadores-descobrem-nova-especie-de-taruma-das-montanhas-do-espirito-santo-e-a-batizam-em-homenagem-a-populacao-pomerana